Blog
-
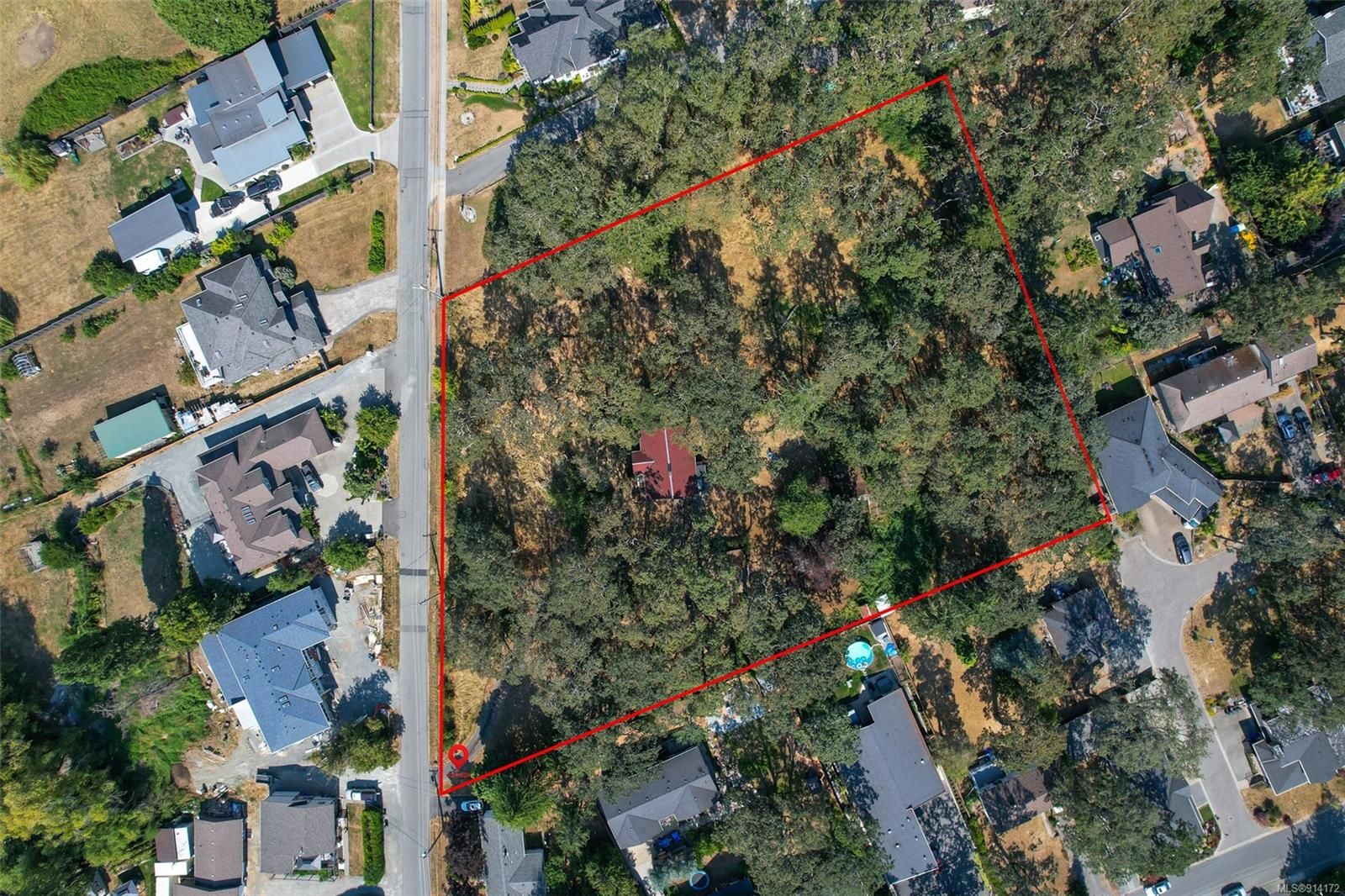
When Housing Debates Erase Ecology: The Story of 4015 Braefoot Rd. and the Garry Oak Ecosystem
By Squirrel for Mayor In spring 2025, a piece of land in Saanich, BC—two acres of former hobby farm at 4015 Braefoot Rd.—became the flashpoint for a wider conflict. A rezoning application proposing 24 townhomes quickly sparked a contentious divide between those focused on increasing housing supply and those alarmed at the ecological cost. But Read more
-

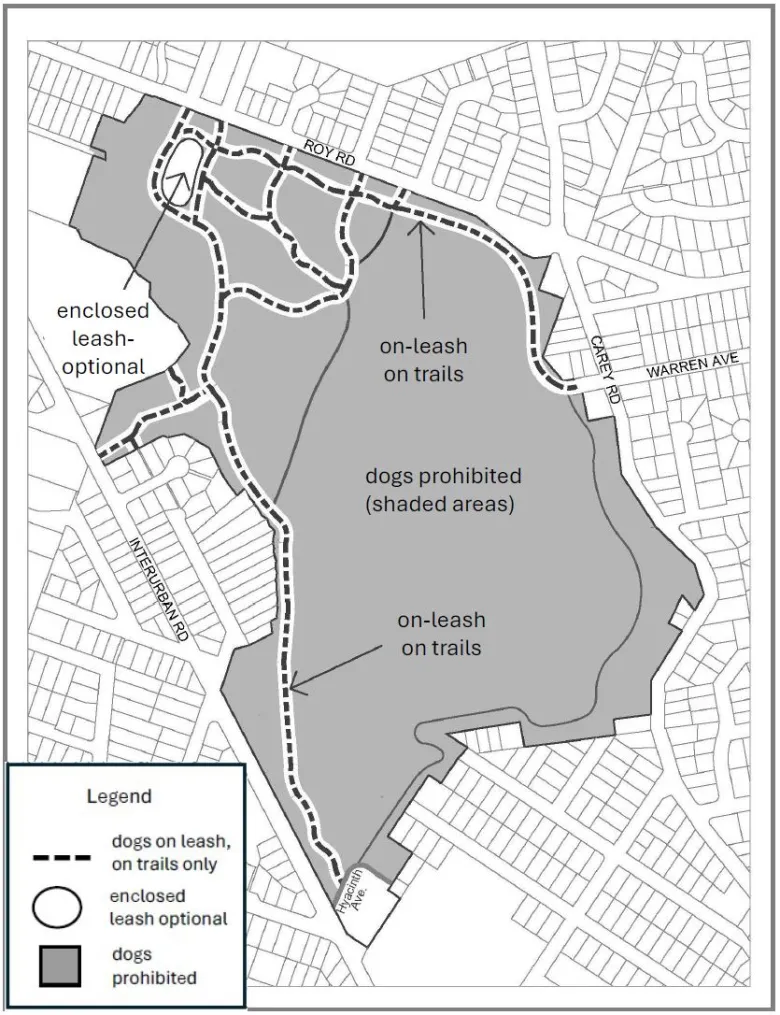
What Does It Mean to Live in an Urban Forest?
By Squirrel For Mayor Living in an urban forest isn’t just about having trees nearby or pockets of green space stitched between streets and buildings. It’s about place—and the many spaces required for life to unfold across species, seasons, and scales. In this short video, we see black-tailed deer teaching their young, a Cooper’s hawk navigating food spaces, Read more
-

Setbacks, Soil, and Survival: Why Urban Forest Protection in Victoria Starts with Space
By Squirrel for Mayor Setbacks are often treated as a technical zoning detail—numbers on a site plan to be minimized in the pursuit of density. In reality, setbacks are one of the most powerful tools a city has to protect its urban forest, safeguard biodiversity, and uphold climate resilience and public safety. In the City Read more
-
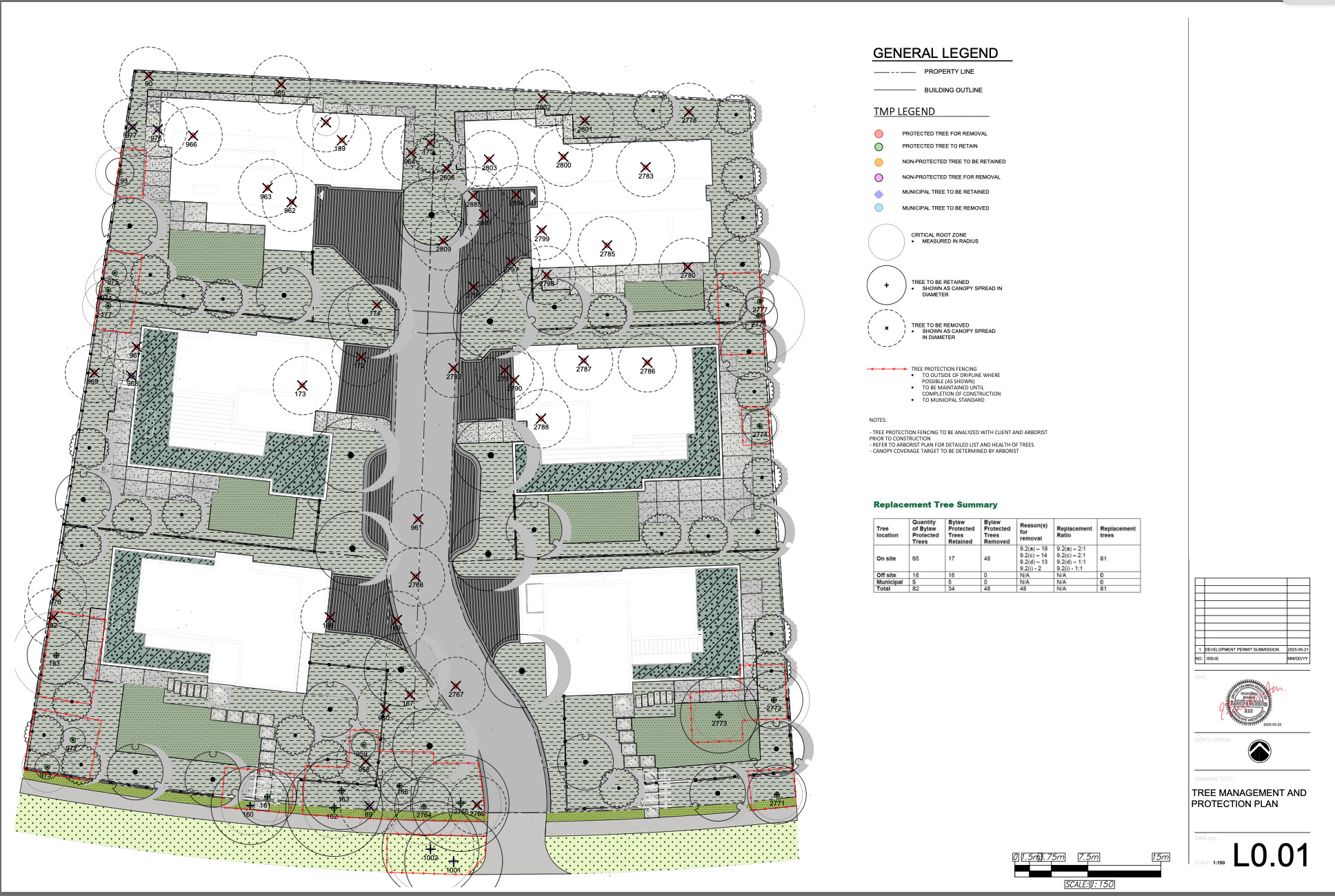
Will Oak Bay Council Allow 48 Bylaw Protected Trees to be Cut for Townhomes in the Uplands? Residents Urge Council to Reject Proposed Development.
By Squirrel for Mayor 2830/2850 Lansdowne Road This proposed development involves two adjacent lots in the Uplands on Lansdowne Road, located on the north side between Ripon Road and Norfolk Road. Both properties are zoned R-2 Residential Use. The purpose of the application is to permit the proposed construction of a Small Scale Multi Unit Read more
-
Urban forests as essential infrastructure for climate resilience and biodiversity: A call to policymakers
Manuel Esperon-Rodriguez, Stefan Arndt, Michael Osei Asibey, Benno Andreas Augustinus, Albert Bach, Monica Ballinas, Victor L. Barradas, David N. Barton, Juergen Bauhus … See all authors First published: 06 November 2025 https://doi.org/10.1002/ppp3.70125 Disclaimer: The New Phytologist Foundation remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in maps and in any institutional affiliations. OPEN LETTER TO POLICYMAKERS AT THE 30TH MEETING OF THE CONFERENCE OF THE PARTIES Read more